Less effort, more insight: introducing Dependency Graph for Supply Chain
Modern software development thrives on open source dependencies, but those dependencies often introduce hidden risks. Vulnerabilities buried in transitive dependencies pose significant challenges and roadblocks for AppSec teams, due to the convoluted web formed by these dependencies. This makes it especially difficult to effectively prioritize and remediate transitive vulnerabilities. Scans also often require custom configuration to run or lockfiles to generate and scan the web of dependencies.
With the introduction of Dependency Graph, we're empowering AppSec engineers to more easily scan, understand, and secure their software supply chain. This foundational technology enables:
Reduction (and in some cases, elimination!) of effort to scan dependencies
Visualization of dependency paths to help prioritize and remediate transitive dependencies
Our new Dependency Graph accomplishes these points through an updated workflow that minimizes reliance on lockfile scans and a new feature we call Dependency Path.
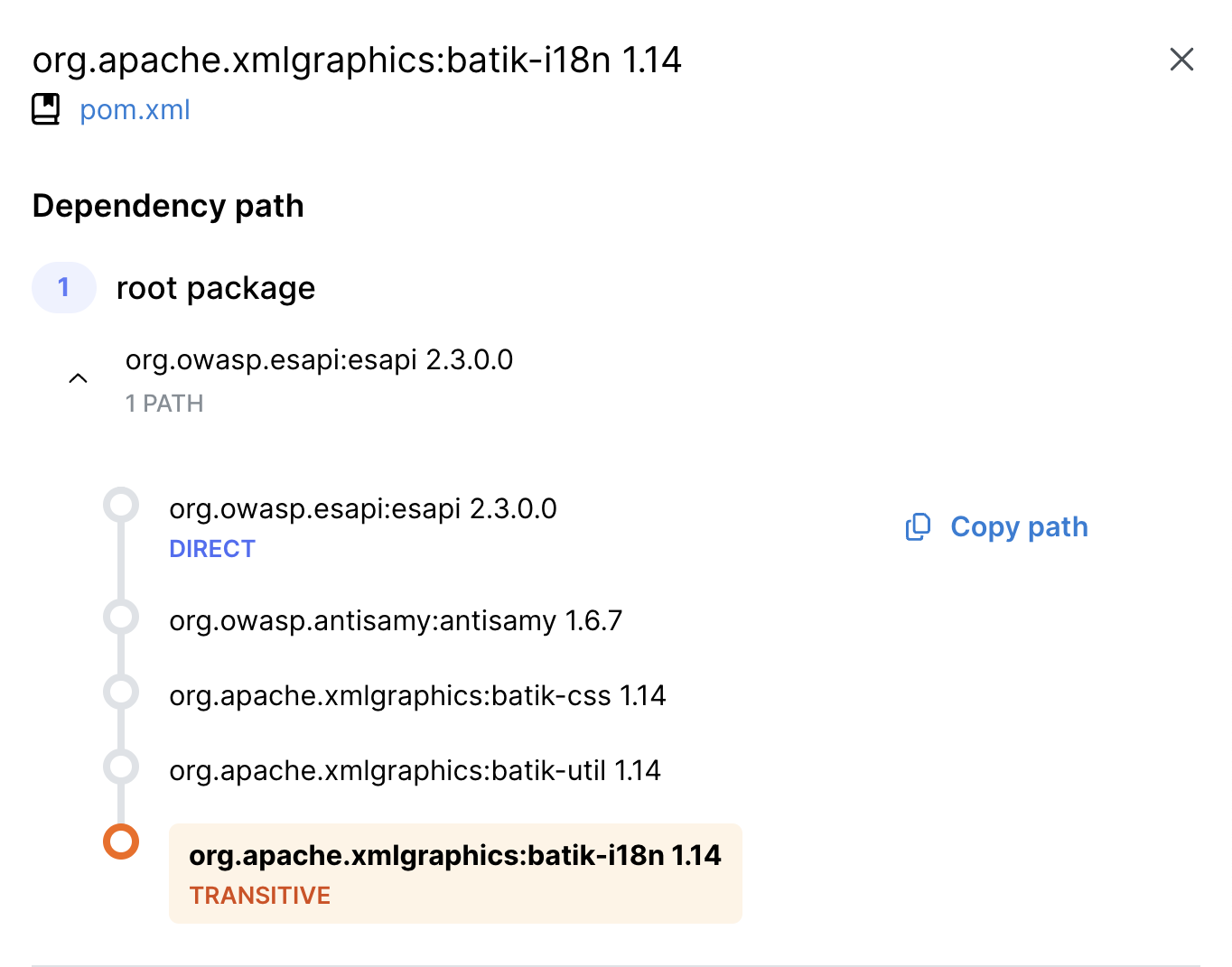
Dependency Paths from Semgrep
Understanding dependency graphs
All software projects depend on external libraries, which in turn may depend on other packages, and so on. Dependencies can be:
Direct dependencies: packages your project explicitly uses
Transitive dependencies: the direct dependencies’ dependencies; relationships inherited through direct dependencies, potentially several layers deep
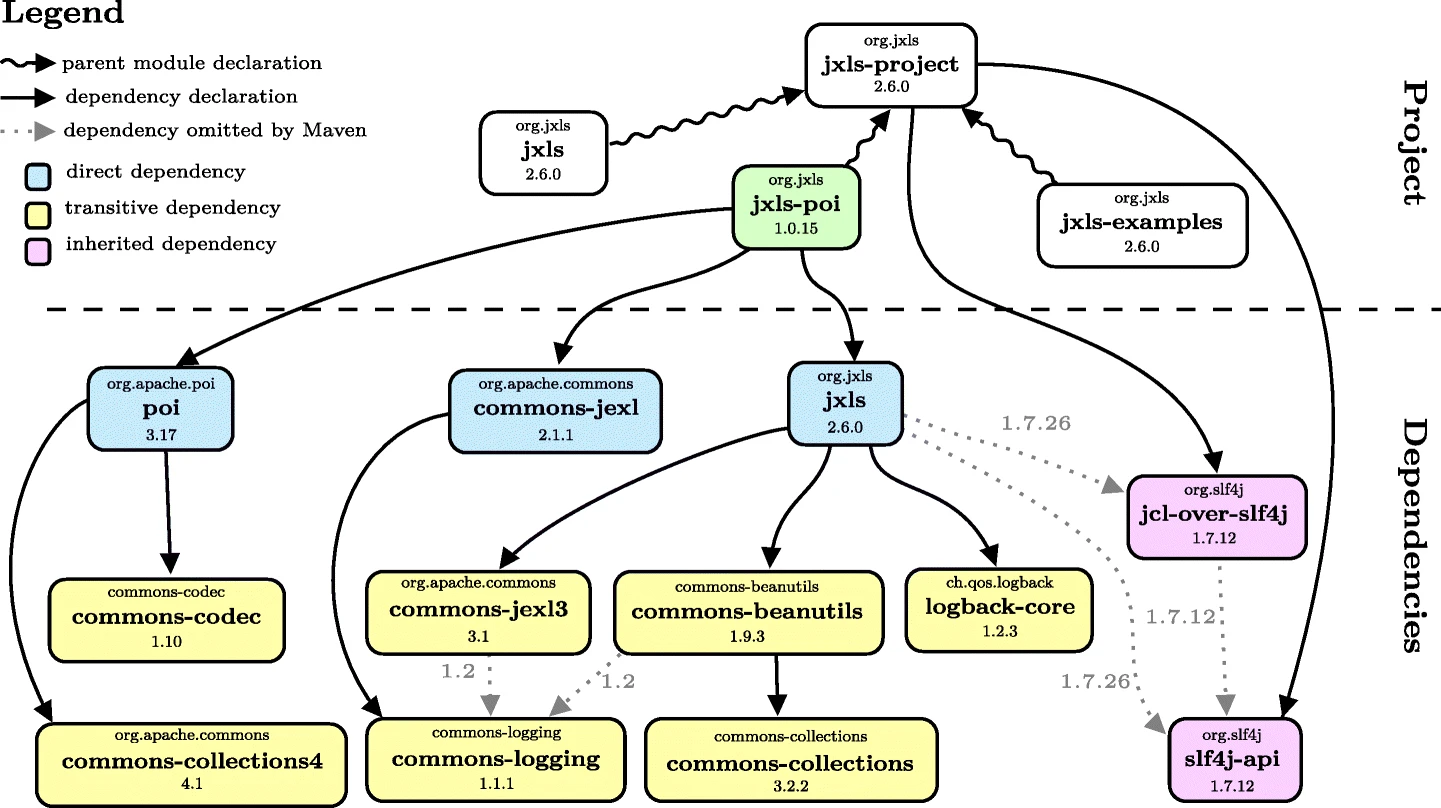
Bloated dependencies in the maven ecosystem. "Fig.1" by César Soto-Valero et al is licensed under CC BY 4.0
The map of all these dependencies and the relationship between them is the dependency graph.
Flexibility with, or without, lockfiles
Lockfiles – compiled dependency manifests that specify the exact version of every dependency installed – are the best investment you can make for supply chain security. They encode information about the dependency graph, the exact versions of dependencies, transitive relationships, and ensure consistent dependency resolution across environments. However, their adoption isn’t universal. While many developer teams embrace them, other teams may avoid them for various reasons: lockfiles may introduce friction in development workflows, they may be uncommon in the programming language/ecosystem that the team uses, or they may result in more frequent merge conflicts which slow down development.
This inconsistency creates a significant challenge for AppSec teams that need to understand the risks introduced by third party dependencies. With the power of our Dependency Graph, Semgrep now adapts to a wider range of real-world scenarios by:
This flexibility significantly reduces the work required to identify vulnerabilities in third-party code, regardless of whether lockfiles are used.
Dependency Path: connect the dots to reduce risk
Dependency relationships form complex webs that are difficult to navigate, which can lead to obscured vulnerabilities buried deep within a project. Prioritization and remediation of transitive vulnerabilities has historically been tedious and labor intensive. Without the right tools, AppSec engineers are left to a cumbersome manual process digging in registries to determine where transitive dependencies exist in their codebase along with where and how they are imported.
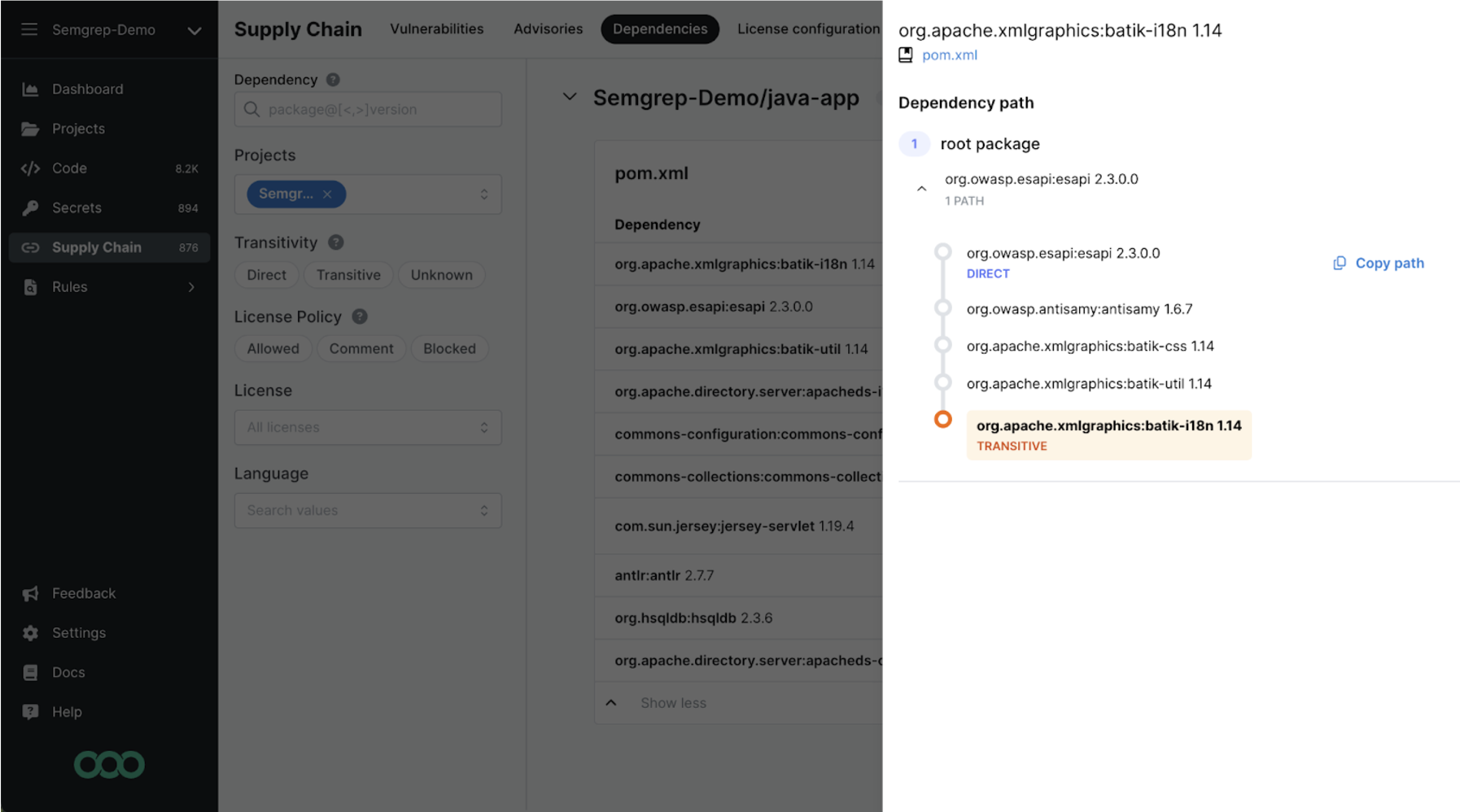 Semgrep now solves this challenge with the Dependency Path feature. To understand how a dependency has been introduced into your project, simply look at a transitive dependency’s path. Easily see which direct dependencies you need to upgrade or replace in order to remediate the vulnerability and secure your code. A direct impact of our visualization is the immediate knowledge of if a transitive vulnerability is only one or many layers deep– which changes both the risk profile and remediation effort– and thus the prioritization.
Semgrep now solves this challenge with the Dependency Path feature. To understand how a dependency has been introduced into your project, simply look at a transitive dependency’s path. Easily see which direct dependencies you need to upgrade or replace in order to remediate the vulnerability and secure your code. A direct impact of our visualization is the immediate knowledge of if a transitive vulnerability is only one or many layers deep– which changes both the risk profile and remediation effort– and thus the prioritization.
This visualization helps automate a critical part of the triage process for transitive vulnerabilities, saves precious time and effort, and enables AppSec teams to focus on higher their ultimate goals: reduction of risk and installing secure guardrails.
Tackling transitive vulnerabilities in practice
Imagine your SCA tool has flagged multiple critical vulnerabilities in the transitive dependency of spring-aop 6.1.11. The AppSec team knows they should remediate this, but they do not know how many layers deep it falls, nor which direct dependencies require an upgrade to remediate the vulnerabilities. In the best case, the vulnerable package is not too deep in the dependency tree. In the worst case, it lives several layers deep and can be used by several other dependencies! A transitive vulnerability this deep requires a very high level of commitment to unravel, not to mention its relatively lower priority when compared to more straightforward vulnerabilities.
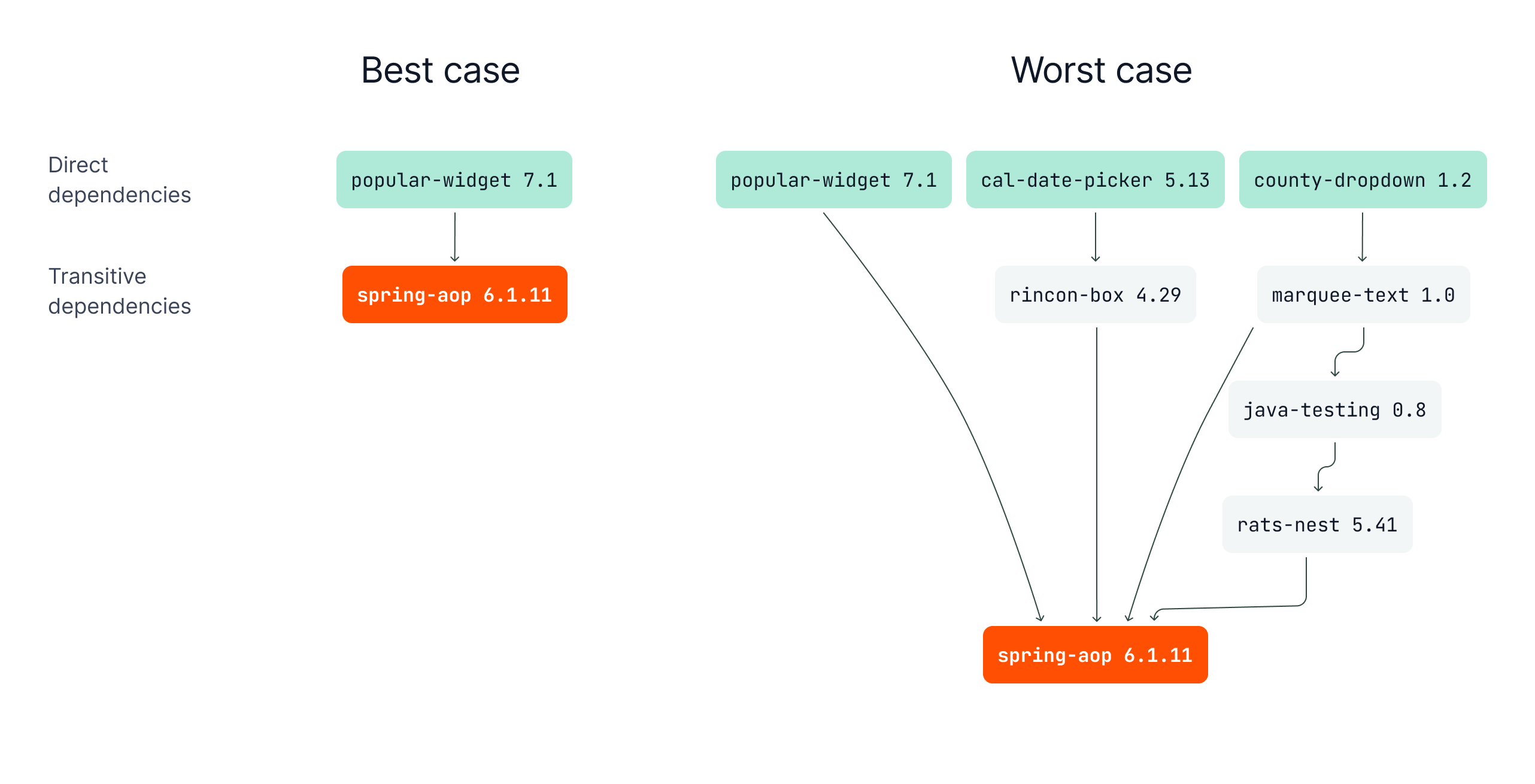
Best and worst case scenarios
Enter Semgrep’s Dependency Path. By visualizing the path of a critical vulnerability through the graph—traced back three layers to a rarely updated library—developers now know exactly which direct dependencies are responsible for introduction of the vulnerable, transitive ones. This map helps prioritize which vulnerabilities to remediate by surfacing how many paths and layers exist.
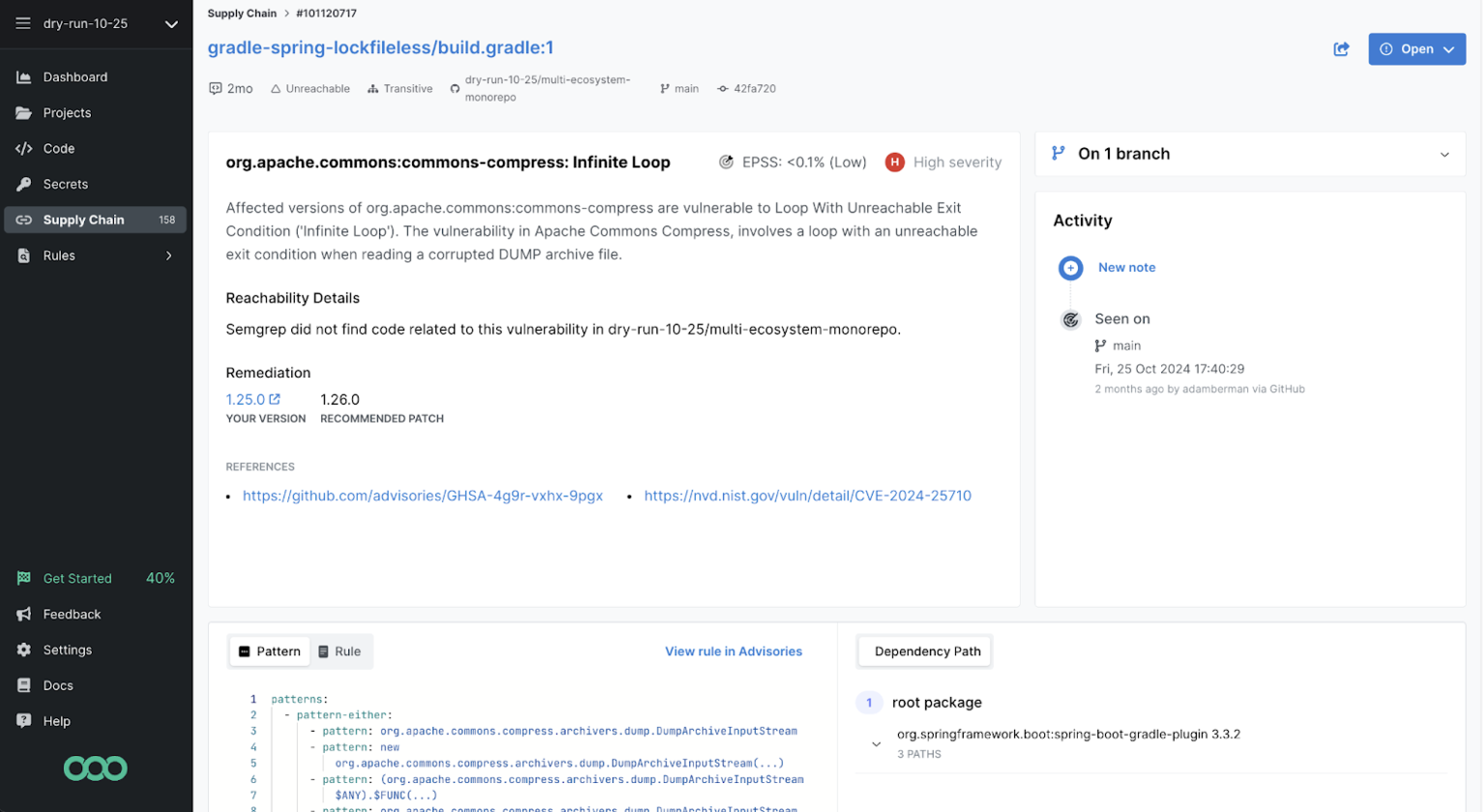
Vulnerabilities page contains links for “Transitive” and prompts the user to click and reveal something awesome
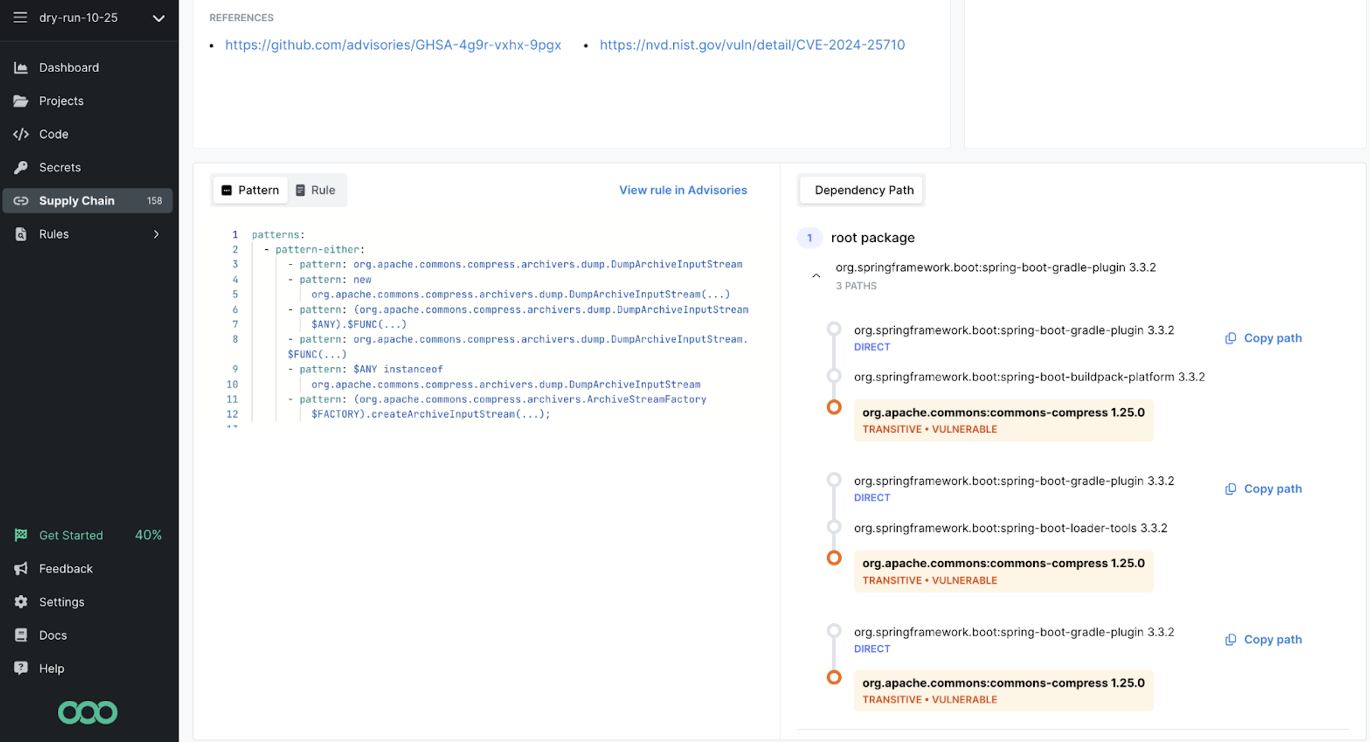
Dependency Path drawer opens and reveals the transitive, and vulnerable, paths
Zooming out, Semgrep’s Dependency Graph gives AppSec engineers the clarity they need to take decisive action. With this feature in their hands, AppSec teams who use Semgrep continue to gain:
Comprehensive visibility: See and understand your software supply chain: all dependencies, direct and transitive, and vulnerabilities in one instance
Reduced noise: Automate triage to focus on remediation and secure guardrails
Empowered developers: Adapt to developer workflows and reduce friction of onboarding repos.
What’s next: less effort, more visibility
A mountain of dependencies comprises modern software — and is at the root of many vulnerabilities. With our Dependency Path, our changes to lockfile scans, and the underlying Dependency Graph, you can reveal your software’s risk profile, reduce the effort needed to find and prioritize vulnerabilities, and protect against threats buried deep in your stack.
As of today, Dependency Graph is live and in public beta! Reach out to your Semgrep contact to test the Dependency Graph on your Semgrep Supply Chain instance. And stay tuned as we continue to expand our breadth of coverage, with support for C# coming soon.
You cannot secure what you cannot see. Start mapping your software territory today with Semgrep Supply Chain.





 Semgrep now solves this challenge with the Dependency Path feature. To understand how a dependency has been introduced into your project, simply look at a transitive dependency’s path. Easily see which direct dependencies you need to upgrade or replace in order to remediate the vulnerability and secure your code. A direct impact of our visualization is the immediate knowledge of if a transitive vulnerability is only one or many layers deep– which changes both the risk profile and remediation effort– and thus the prioritization.
Semgrep now solves this challenge with the Dependency Path feature. To understand how a dependency has been introduced into your project, simply look at a transitive dependency’s path. Easily see which direct dependencies you need to upgrade or replace in order to remediate the vulnerability and secure your code. A direct impact of our visualization is the immediate knowledge of if a transitive vulnerability is only one or many layers deep– which changes both the risk profile and remediation effort– and thus the prioritization.





