Use GitHub repository rulesets to implement Semgrep
Use GitHub repository rulesets to quickly implement Semgrep scans across hundreds or thousands of repositories in your GitHub organization.
Repository rulesets allow you to add a Semgrep scan as a workflow that is required for pull requests to pass before merging. Formerly, this feature was called required workflows.
Repository rulesets use a centralized workflow file to execute the Semgrep scan action, meaning you can run scans on pull requests in as many repositories as desired by creating a single file.
Set up the central Semgrep scan workflow
To use the Semgrep workflow in other repositories owned by your organization, you can create a new repository in the organization with the Semgrep workflow file, or add it to an existing repository where you store common workflows. This example describes creating the workflow in a new repository called semgrep-workflow.
- Create a new repository following the GitHub documentation.
- Name the repository
semgrep-workflow. - Choose the repository visibility that matches the widest visibility of the repositories you want to run the workflow in. For example, if you want to run Semgrep on public, internal, and private repositories, the repository containing the workflow file must be public.
- Add the Semgrep workflow file to the repository at
.github/workflows/semgrep.yml. You can use the sample configuration provided in the documentation, or a custom configuration.
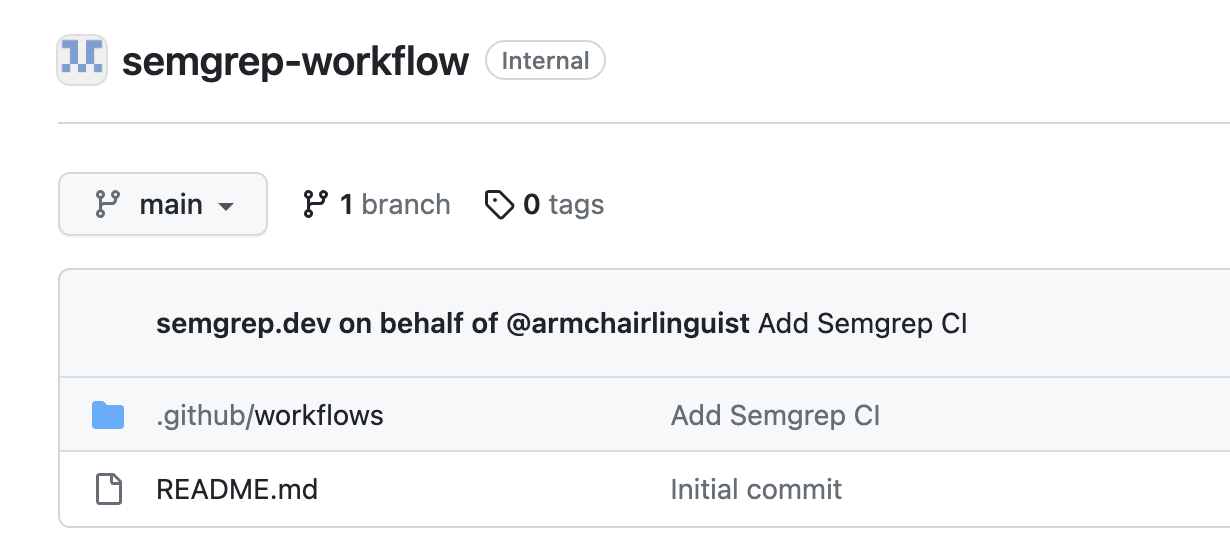
This example repository is internal, so it can only be used to store workflows that run on internal and private repositories.
Behavior with bot-initiated commits
The default Semgrep GitHub Actions configuration excludes any PRs or commits from GitHub's dependabot to prevent permissions errors. If you have other bots or automations active in your organization's workflows, consider excluding these bots as well. Otherwise, the action may error due to bot permissions, or it may simply not be useful to run a Semgrep scan on changes made by an automation. For example, to exclude both dependabot and other GitHub Actions, include:
if: github.actor != 'dependabot[bot]' && github.actor != 'github-actions'
Recommended configuration with merge queues
If you use merge queues for repositories scanned with this workflow, your config must include merge_group as a trigger in the on: block. Otherwise, the workflow cannot run in the merge queue and can block the queue.
Unlike for pull_request event types, Semgrep does not have any automatic configuration to run diff-aware scans on merge_group events, so additional configuration is needed to run diff-aware scans in this environment. The most straightforward solution is to configure the workflow to be skipped during the merge group check, since the primary goal of a Semgrep diff-aware scan is to inform the developer before merging if they are introducing security issues.
With the recommended alterations and removal of event types that do not occur with repository rulesets, the sample configuration would look like this:
name: Semgrep
on:
pull_request: {}
workflow_dispatch: {}
merge_group:
types: [checks_requested]
jobs:
semgrep:
name: semgrep/ci
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
container:
image: semgrep/semgrep
# Skip any PR created by dependabot and any check triggered by merge group
if: (github.actor != 'dependabot[bot]') && (github.event != 'merge_group')
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- run: semgrep ci
env:
SEMGREP_APP_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SEMGREP_APP_TOKEN }}
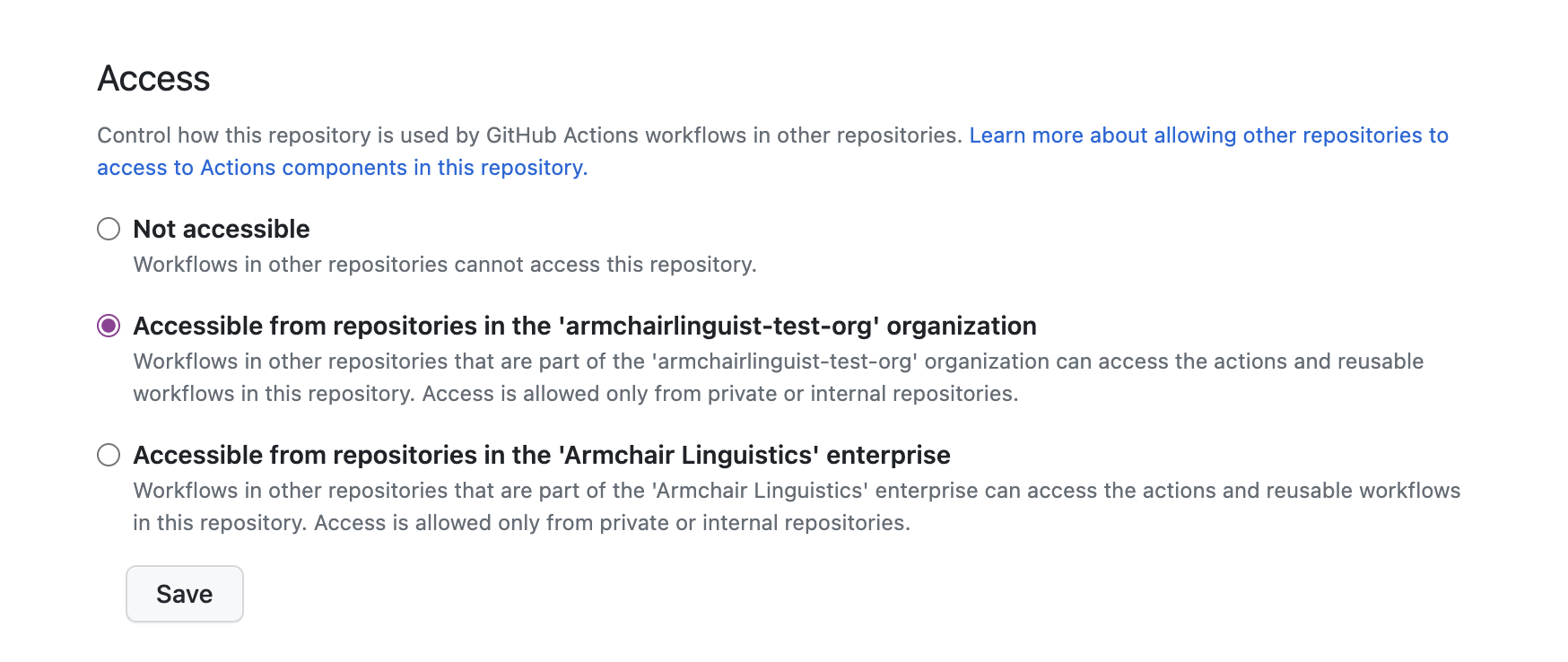
Configure repository workflow access
The repository containing the Semgrep workflow must allow access to workflows from other repositories in the organization.
To configure access:
- In the repository containing the Semgrep workflow, click Settings > Actions > General.
- In the Access section, select one of the Accessible from options to make the repository workflows accessible to your organization.
Configure an organization secret
To run a scan using semgrep ci, Semgrep requires a valid token. When configuring Semgrep as a required workflow for multiple repositories, set up the token as an organization secret.
If you use a custom semgrep.yml configuration, ensure you refer to the secret as ${{ secrets.SEMGREP_APP_TOKEN }} in your configuration. For the required workflow, this refers to the organization secret.
- Click Create new token on Settings > Tokens in the Semgrep AppSec Platform.
- Ensure the Agent (CI) scope is checked for the token.
- Copy the token value for use on GitHub, and click Save.
- Create an organization secret, following the GitHub documentation.
- Name the secret
SEMGREP_APP_TOKEN. - Paste the value you copied from the Semgrep AppSec Platform.
- Select a value for Repository access that matches the repositories you intend to scan with the workflow.
- Click Add secret.
Create an organization ruleset
To create the ruleset:
- Go to your GitHub organization page and click Settings.
- Under Code, planning, and automation, click Repository and then Repository rulesets.
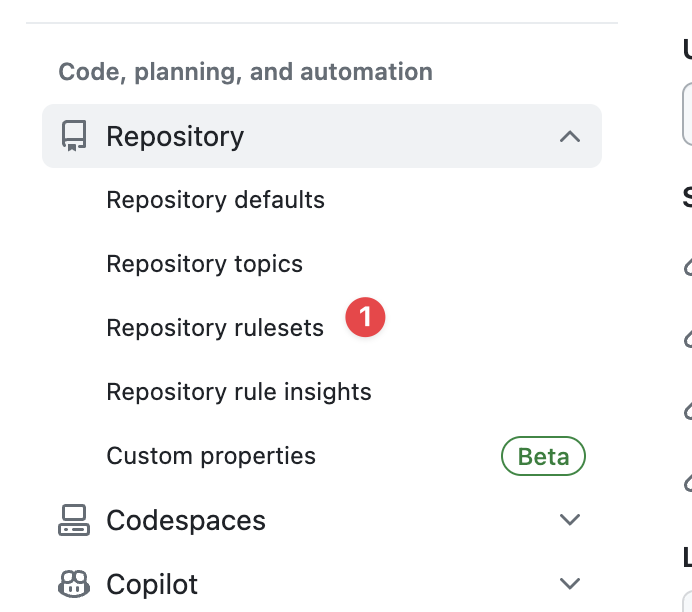 .
. - Click New branch ruleset.
- Configure the enforcement status, bypass list, target repositories, and target branches based on your organization policies.
- Under Branch protections, check the box Require workflows to pass before merging.
- Click Add workflow.
- In the Add required workflow modal, select the repository where you placed the Semgrep workflow.
- Then, select the branch, tag, or commit to use.
- In the Pick a workflow file field, click and select the Semgrep workflow you created in Setting up the central Semgrep scan workflow.
- Click Add workflow.
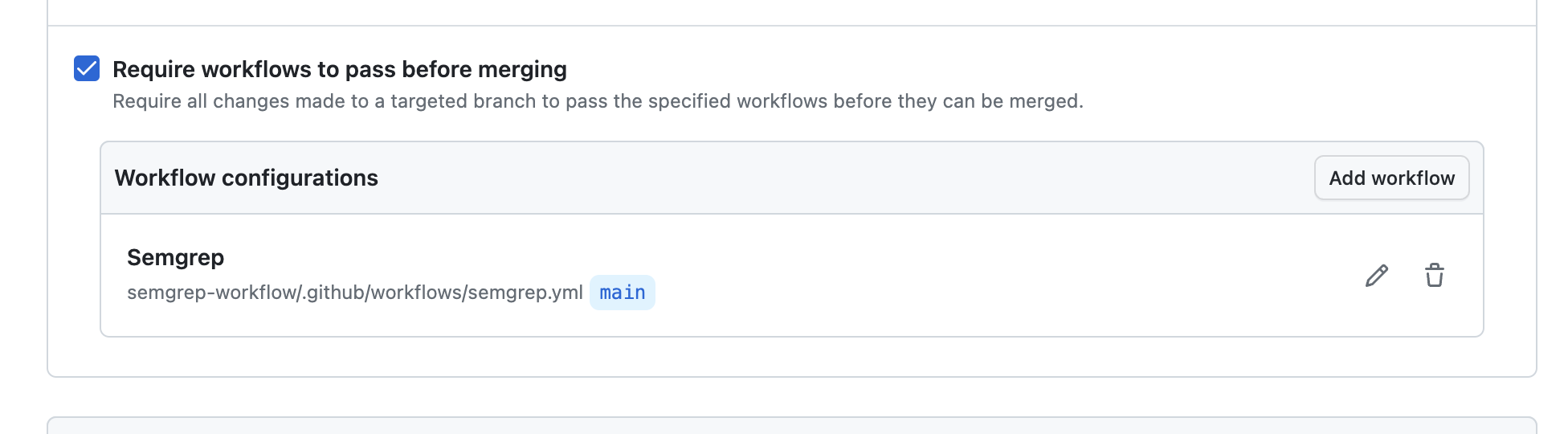
- Click Create to create the ruleset.
Refer to GitHub's Creating rulesets for repositories in your organization for more general guidance on creating a ruleset for your organization.
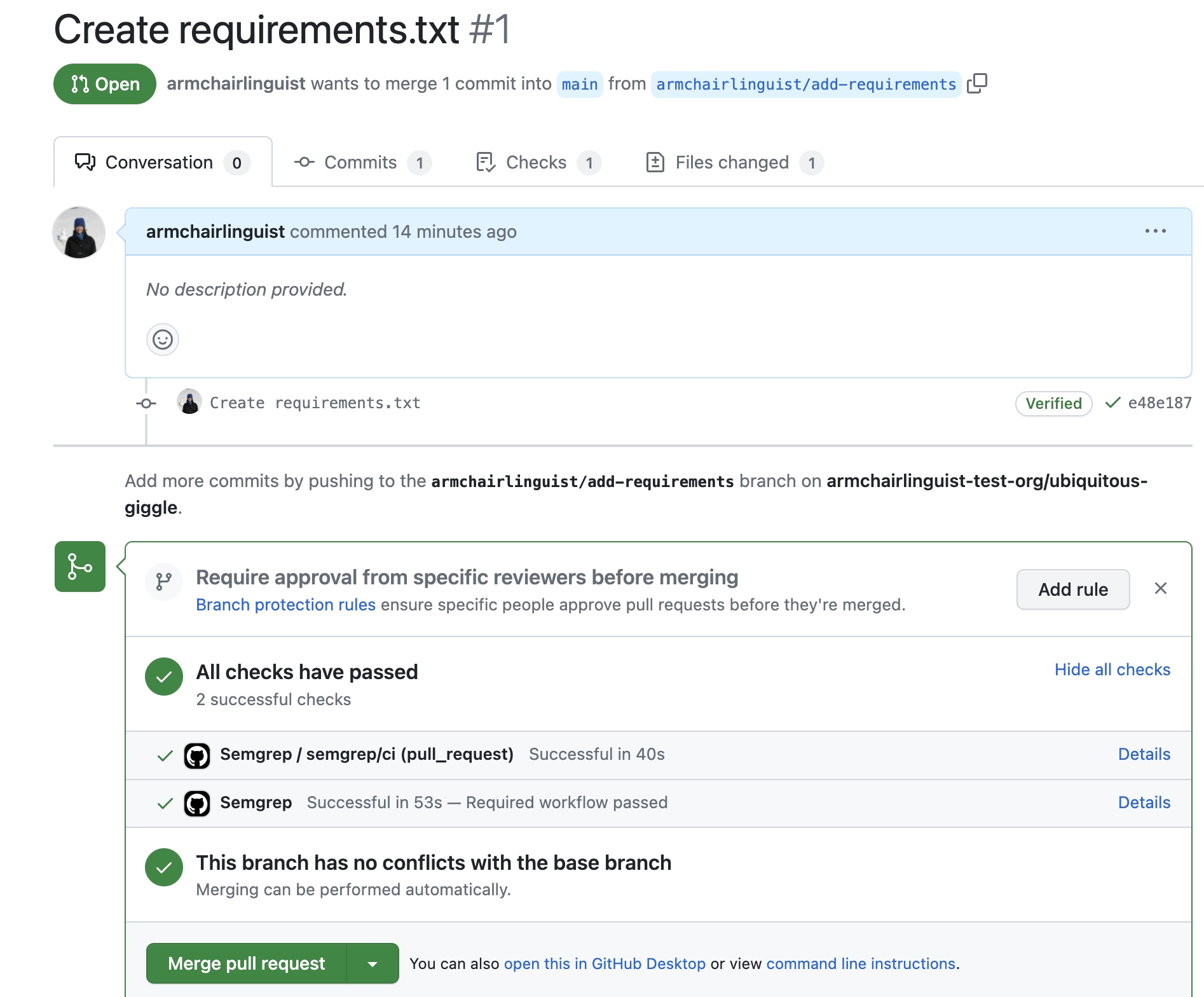
Verify by creating a pull request
After completing the preceding steps, create a pull request in an affected repository to verify the workflow runs as expected.
- Identify a repository targeted by the organization ruleset you created in the previous section.
- Create a pull request in that repository, following the GitHub documentation.
- After creating the pull request, review the checks and ensure the Semgrep workflow ran as expected.
The required workflow allows merge if the scan is successful, or blocks the pull request if the scan has blocking findings.
Limitations
Workflows required by repository rulesets are only triggered by pull_request or merge_group events. When triggered for a pull request, Semgrep runs a diff-aware scan, which only scans changed files.
To run full scans (scan all files) for your organization's repositories as well, you would need to supplement this setup with another approach, such as reusable workflows.
Not finding what you need in this doc? Ask questions in our Community Slack group, or see Support for other ways to get help.