Triage and remediate Supply Chain findings
At least one repository that scans for dependencies through Semgrep Supply Chain. See Scan third-party dependencies.
Once Semgrep Supply Chain successfully scans your repository and you've viewed your results, you can triage and remediate the findings presented in Semgrep AppSec Platform using the Supply Chain page.
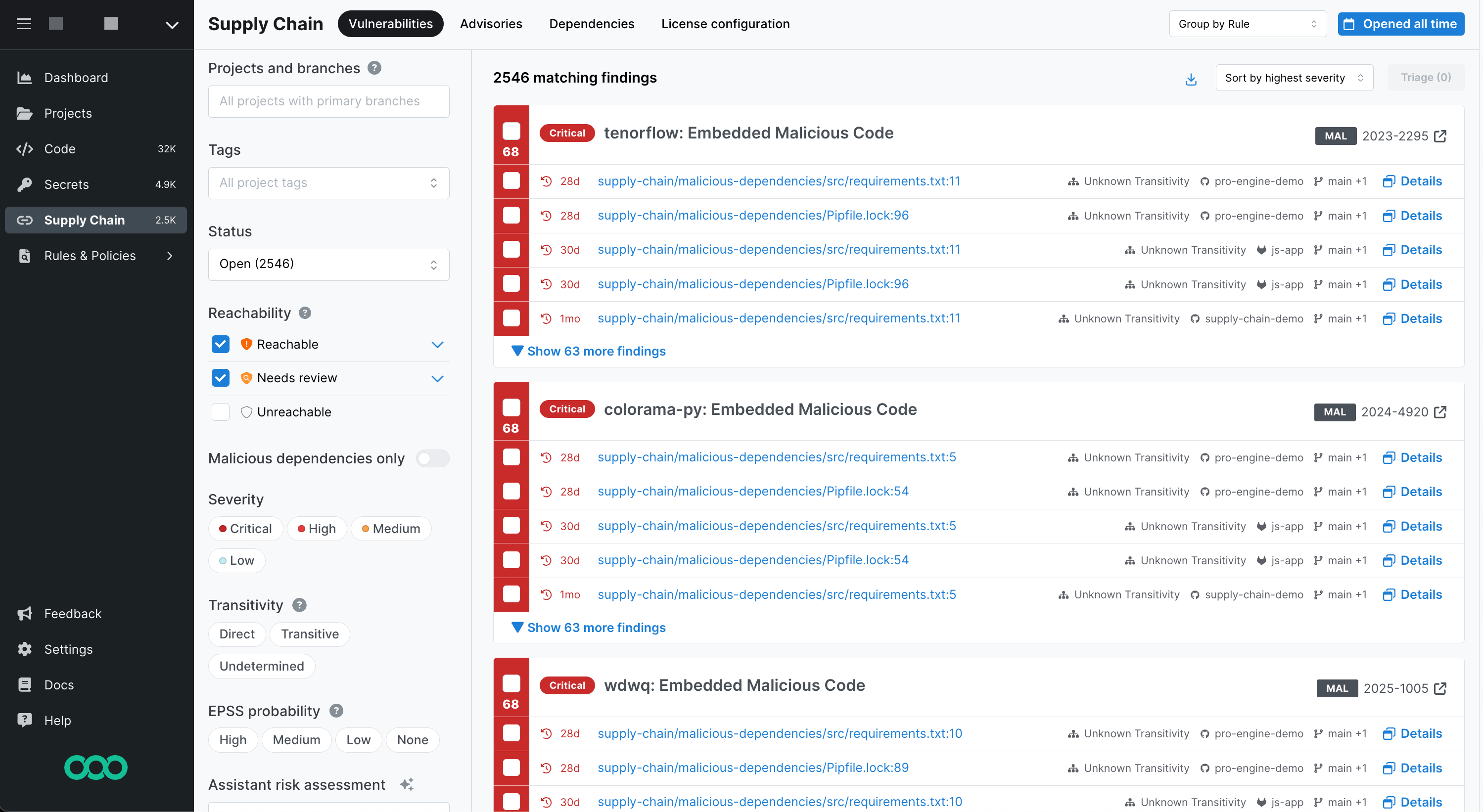 Figure. Semgrep Supply Chain Vulnerabilities page.
Figure. Semgrep Supply Chain Vulnerabilities page.
Triage and remediate findings
Once you have viewed the Supply Chain findings, you can triage them for further work by your AppSec team, including remediation. Semgrep Supply Chain provides the following methods to help you assess your findings:
| Assessment action | Method |
|---|---|
| View the dependency paths for a transitive dependency. | Visible on the vulnerability entry. |
| View specific pattern matches in your codebase. | Click the link provided in the vulnerability entry to see where the issue appears in the source code. |
| View specific CVE entries in cve.org. | Click the vulnerability's CVE badge. |
| View safe versions to upgrade your dependencies. | Visible on the vulnerability entry. |
| Filter vulnerabilities. | Click any of the filters available. Refer to the following table for filtering information. |
Remediate true positives
Remediate (or resolve) true positives in Semgrep Supply Chain through the following methods:
- Update the dependency to a safe version that does not contain the vulnerability.
- Remove the dependency and refactor all usages in the codebase.
Upgrade guidance uses AI to analyze Semgrep scans to see if the fixed versions of a dependency are safe to upgrade to or may cause breaking changes in the code. It can create a PR to upgrade the dependency to the fixed version.
This feature is in private beta. For users with an existing Semgrep plan, reach out to support to join the beta.
Remove the dependency and refactor the code
Removing the dependency and refactoring the code is another method to remediate vulnerabilities. Upon merging any dependency removals, Semgrep Supply Chain scans the PR or MR, detects the changes in your manifest file or lockfile, and updates the status to Fixed.
Ignore findings
The Vulnerabilities tab allows you to identify the reachable, true positives so that you can fix or resolve the related issues. However, you can ignore any false positives, acceptable risks, or deprioritized findings due to some factor. To do this:
- Select one or more findings.
- Click Triage.
- Select Ignore and click Continue.
- Select an Ignore reason, provide a optional comment, and click Ignore.
Block pull request or merge requests
To block or leave comments on pull request or merge requests, see the Supply Chain Policies document.
Not finding what you need in this doc? Ask questions in our Community Slack group, or see Support for other ways to get help.