Overview
Semgrep Supply Chain is a software composition analysis (SCA) tool that detects security vulnerabilities in your codebase introduced by open source dependencies. It can also:
- Generate a software bill of materials (SBOM) that provides a complete inventory of your open source components
- Query for information about your dependencies
- Support the enforcement of your business' open source package licensing requirements
- Detect malicious dependencies (currently in private beta; reach out to support to join the program)
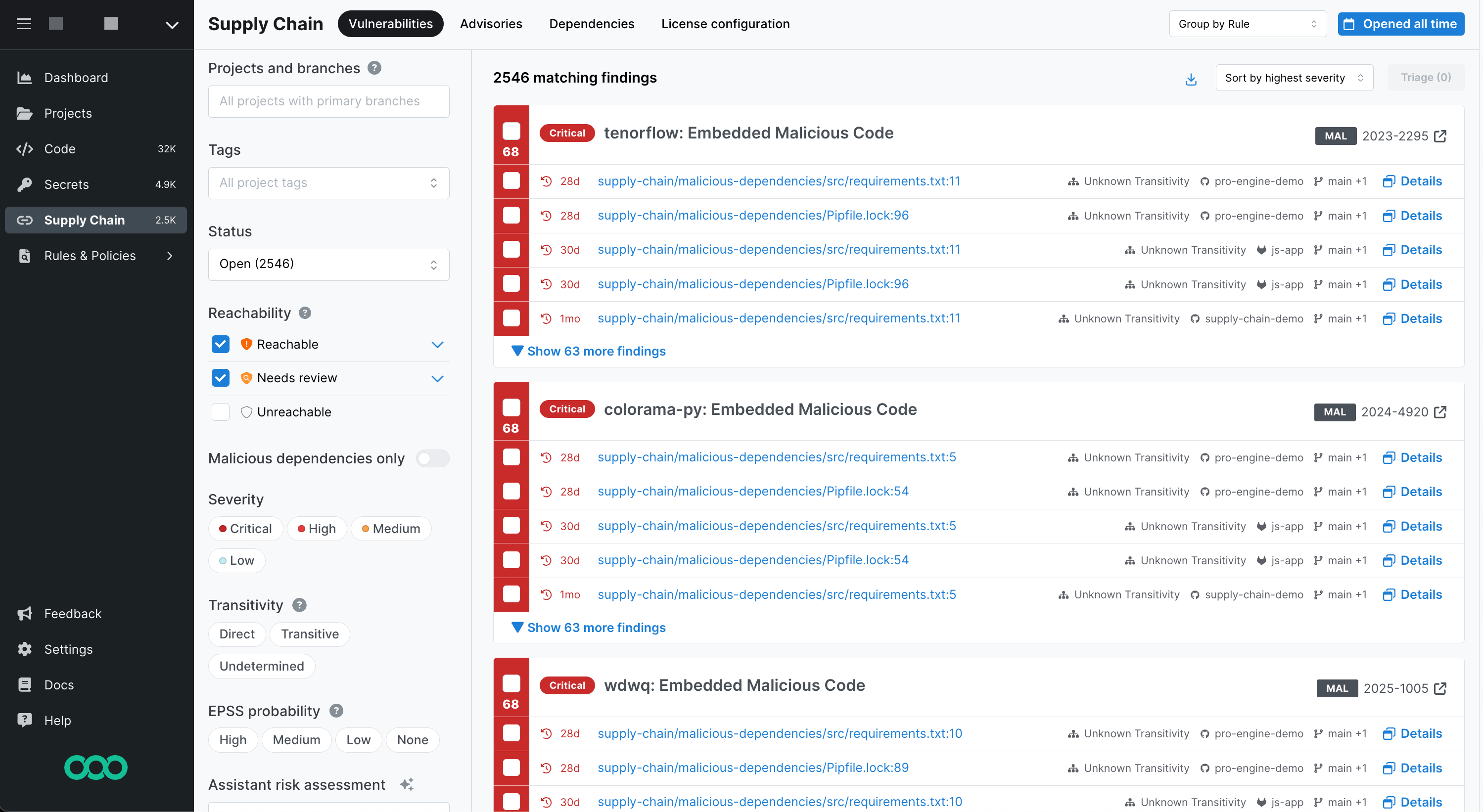 Figure. Semgrep Supply Chain Vulnerabilities page.
Figure. Semgrep Supply Chain Vulnerabilities page.
Open source security vulnerabilities
Semgrep Supply Chain detects security vulnerabilities in your codebase introduced by open source dependencies using high-signal rules, which are instructions Semgrep uses detect patterns in code, to determine the vulnerability's reachability.
To do this, Semgrep Supply Chain parses manifest files or lockfiles for a list of dependencies, then scans your codebase using rules that specify the following information:
- The dependency versions that contain a vulnerability
- The pattern for the vulnerable code that Semgrep compares against your code
- The severity of the vulnerability
The following diagram shows the relationship between a Semgrep Supply Chain rule, the codebase scanned, and its manifest file or lockfile:
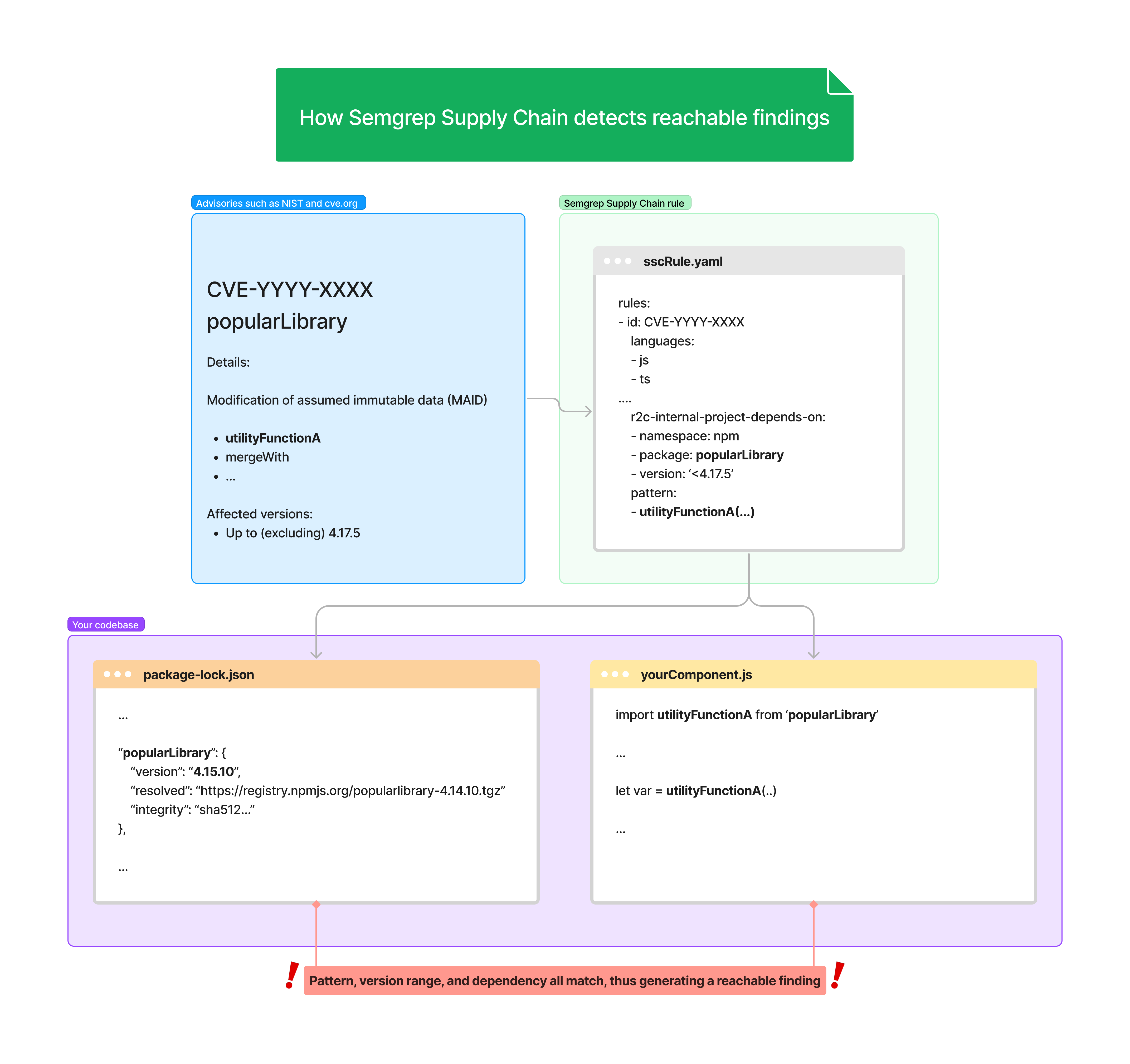 Figure. Relationship between a Supply Chain rule, manifest file or lockfile, CVE record, and codebase.
Figure. Relationship between a Supply Chain rule, manifest file or lockfile, CVE record, and codebase.
Semgrep Supply Chain rule update frequency
Semgrep ingests CVE information and security advisories from the following sources:
Semgrep processes new information at least once per day to:
- Generate rules for new security advisories
- Update rules based on changes to existing security advisories
Types of Semgrep Supply Chain findings
Semgrep Supply Chain generates a finding whenever it determines that your codebase uses or imports a package containing a vulnerability. In addition, Semgrep supports reachability for generally available (GA) languages:
- GA languages: Semgrep writes rules for all critical and high CVE severity levels for GA languages. That means Semgrep Supply Chain can flag all your critical/high-severity findings as either reachable or unreachable.
- If there's a code pattern in the codebase that matches the vulnerability definition, the finding is flagged as reachable.
- A finding is always reachable if the only way to fix the vulnerability is to upgrade the dependency. Semgrep strongly recommends upgrading the dependencies involved in these findings.
- A finding is conditionally reachable if the vulnerability can be exploited when specific conditions are met. The finding is reachable if, in addition to the dataflow reachability in code, additional factors, such as the use of a specific operating system, are met. Semgrep cannot determine whether such factors are true, so conditionally reachable findings require manual review.
- If Semgrep Supply Chain determines that you don't use the vulnerable library package imported or you don't use the vulnerable piece of code of the library or package imported, the finding is flagged as unreachable.
- If Semgrep Supply Chain determines that you use a vulnerable version of a dependency, but Semgrep Supply Chain doesn't have a relevant reachability rule, it flags the finding as no reachability analysis.
- If there's a code pattern in the codebase that matches the vulnerability definition, the finding is flagged as reachable.
- For languages where Semgrep Supply Chain doesn't currently offer rules with reachability analysis languages, Semgrep Supply Chain's performance is comparable to that of GitHub's Dependabot. Semgrep Supply Chain generates these findings by checking the dependency's version listed in your manifest file or lockfile against a list of versions with known vulnerabilities, but it does not run reachability analysis. Because Semgrep Supply Chain doesn't run reachability analysis, it can't determine whether the vulnerability is reachable. Such vulnerabilities are, therefore, flagged as no reachability analysis.
Specific dependency and code match findings are called usages. Semgrep AppSec Platform groups all usages together by vulnerability. For each vulnerability, the UI also displays a CVE number corresponding to the CVE program record.
Transitive dependencies and reachability analysis
A transitive dependency, also known as an indirect dependency, is a dependency of a dependency. Semgrep Supply Chain scans transitive dependencies for all supported languages, looking for security vulnerabilities, but it does not perform reachability analysis. This means that Semgrep Supply Chain doesn't check the source code of your project's dependencies to determine if their dependencies produce a reachable finding in your code.
However, some dependencies are vulnerable simply through their inclusion in a codebase; in such cases, Semgrep Supply Chain generates reachable findings involving these dependencies, even if they're transitive, not direct, dependencies.
Some package ecosystems allow the use of a transitive dependency as if it were a direct dependency. Though this feature is uncommon, Semgrep Supply Chain can scan for such usages and flag vulnerabilities in transitive dependencies as unreachable if not used directly.
Software bill of materials
Semgrep Supply Chain can generate a software bill of materials (SBOM), a complete inventory of your third-party or open source components, to assist you with your auditing procedures.
Dependency search
Semgrep Supply Chain's dependency search feature allows you to query for dependencies in your codebase; it can detect direct and transitive dependencies in any repository on which you have run a full scan. The results list the dependency, along with all of the repositories that use the dependency.
License compliance
The license compliance feature ensures that you're only using open source packages whose licensing meets your organization's requirements.
Malicious dependencies detection
Semgrep can detect malicious dependencies, which are treated as critical severity findings. If you have set up your policies to block critical severity findings, Semgrep prevents developers from merging pull requests or merge requests with malicious dependencies.
Next steps
Semgrep Supply Chain automatically scans repositories that you have added to Semgrep AppSec Platform. Once your first scan is completed:
- View, triage, and remediate your Supply Chain findings.
- Customize Semgrep Supply Chain to ignore files and dependencies to support your security and business goals.
- Generate a software bill of materials (SBOM).
- Query for dependencies in your codebase using dependency search.
- Ensure that you're only using open source packages whose licensing meets your organization's requirements.
Not finding what you need in this doc? Ask questions in our Community Slack group, or see Support for other ways to get help.