May 2023
The following updates were made to Semgrep in May 2023.
These release notes include updates made by Semgrep, Inc. from May 2023 until June 9. Due to the importance of the launch week at the beginning of June 2023, we decided to include the most important updates from the launch also on the release notes page that you are now reading.
Semgrep tiers
- Semgrep’s Community Tier has been sunsetted. Existing and new users now have access to all Semgrep Team tier features for free, subject to usage limits.
Semgrep Cloud Platform
- Semgrep Playground Turbo mode is now in beta. This new mode enables users to create rules using the Semgrep OSS engine which will automatically run upon detecting any change in the rule or sample code. There is no need to click a Run button in Turbo mode.
- Semgrep Zero-config Scanning for GitHub.com is now in beta. Onboard or add many repositories to the Semgrep Cloud Platform without having to commit a CI file for every repository! Reach out to sales@semgrep.com to try it out.
- Role-based access control (RBAC) is now available to all Team tier users, subject to usage limits.
- Single Sign-On (SSO) is now available to all Team tier users, subject to usage limits.
- Improved the UI on the Settings page.
Semgrep OSS Engine
This section of release notes includes upgrades of Semgrep OSS Engine for versions ranging between 1.21.0 and 1.26.0.
-
Kotlin language support update: Kotlin now upgraded from beta support to full GA support! Additionally, as a part of this update for Kotlin:
- Added named ellipses, as
$...X. - Added literal metavariables, from patterns like
"$FOO". You can still match strings that only contain a single interpolated ident by using the brace notation, e.g."${FOO}". - Interpolated identifiers in strings, such as
$foo, are now properly able to match explicitly interpolated expressions, such as${...}.
- Added named ellipses, as
-
Added experimental support for the programming language Cairo 1.0. Thanks to Frostweeds (Romain Jufer) for his contribution!
-
Added experimental support for the programming language Julia.
-
Java support improvement: Semgrep OSS Engine now includes heuristics based on the Java standard library and common naming patterns. As a result, Semgrep OSS Engine can now determine more types of Java expressions, for use with Typed Metavariables.
-
We are introducing a new experimental generic matching engine Aliengrep as an alternative to the default generic mode engine (Spacegrep). Generic mode is used for languages that are not supported by Semgrep OSS Engine. Try out Aliengrep and let us know what you think about it!
-
Taint analysis updates:
-
In Java, Semgrep OSS Engine can now track taint through more get and set methods (getters and setters). Before this update, taint analysis of Semgrep OSS Engine could already relate setters to getters (for example:
o.setX(taint); o.getX(). With this update, it can relate setters and getters to properties (for exampleo.setX(taint); o.x). -
Added experimental options
taint_assume_safe_booleansandtaint_assume_safe_numbersto avoid propagating taint that comes from expressions with boolean or number (integer, float) types. -
Semgrep OSS Engine can recognize that an object constructed by
new Obj("tainted", "safe")has itsxattribute tainted, whereas itsyattribute is safe. -
Extract mode: users can now choose to include or exclude rules to run on, similar to
paths:.For example, to only run the rules on
example-1andexample-2:rules:
- id: test-rule
mode: extract
rules:
include:
- example-1
- example-2To run the rule on everything except
example-1andexample-2:rules:
- id: test-rule
mode: extract
rules:
exclude:
- example-1
- example-2(GitHub issue #7858)
-
-
Semgrep OSS Engine Language Server updates. The following two updates are also related to Semgrep Visual Studio Code extension:
- Support for search and replace with rule patterns through semgrep/search.
- Language Server now notifies you about errors and includes a reason for the crash.
-
Relaxed restrictions on symbolic propagation so that symbolic values survive branching statements. Now (with symbolic-propagation enabled)
foo(bar())matches the following code:def test():
x = bar()
if cond:
exit()
foo(x)
The Semgrep OSS Engine section of release notes mentions only selected additions and changes, for specific bug fixes, see Semgrep OSS Engine GitHub changelog and search for Fixed sections under each version.
Semgrep Supply Chain
- Semgrep Supply Chain’s License compliance feature is now in beta. This feature enables developers to view the licenses of dependencies in all repositories that are scanned by Semgrep Supply Chain. Read the documentation: License compliance.
- This feature also enables security engineers to Block, leave a Comment, or Allow dependencies when a PR introducing the dependency is first opened, based on the license of the dependency.
- License compliance supports many popular Copyleft, Weak-copyleft, and Permissive licenses. Other licenses can also be detected.
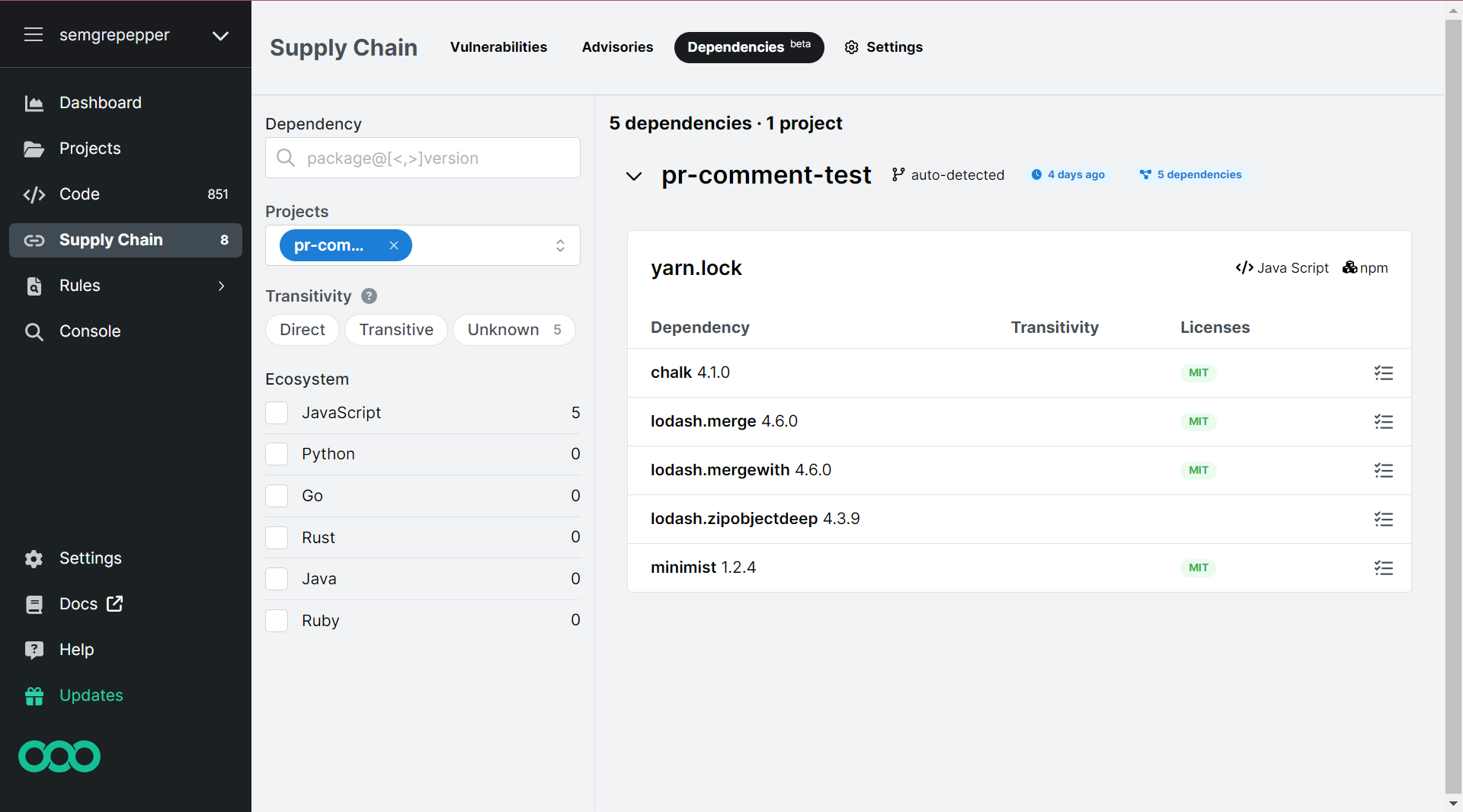
- Semgrep Supply Chain is now available for free to Team tier users, subject to usage limits.
- Improvements to Semgrep Supply Chain Dependencies page.
Semgrep Visual Studio Code
Semgrep Visual Studio Code extension received new updates! Try to scan your code using the extension and let us know what we can improve. See more in Semgrep Visual Studio Code extension documentation. This extension allows you to check your code for vulnerabilities within seconds, with every line of code changed in the editor. The extension is built on Language Server Protocol, so you can hack it for other editors of your choice. The extension also has a dedicated changelog on GitHub so you can always see the latest updates.
Semgrep Code
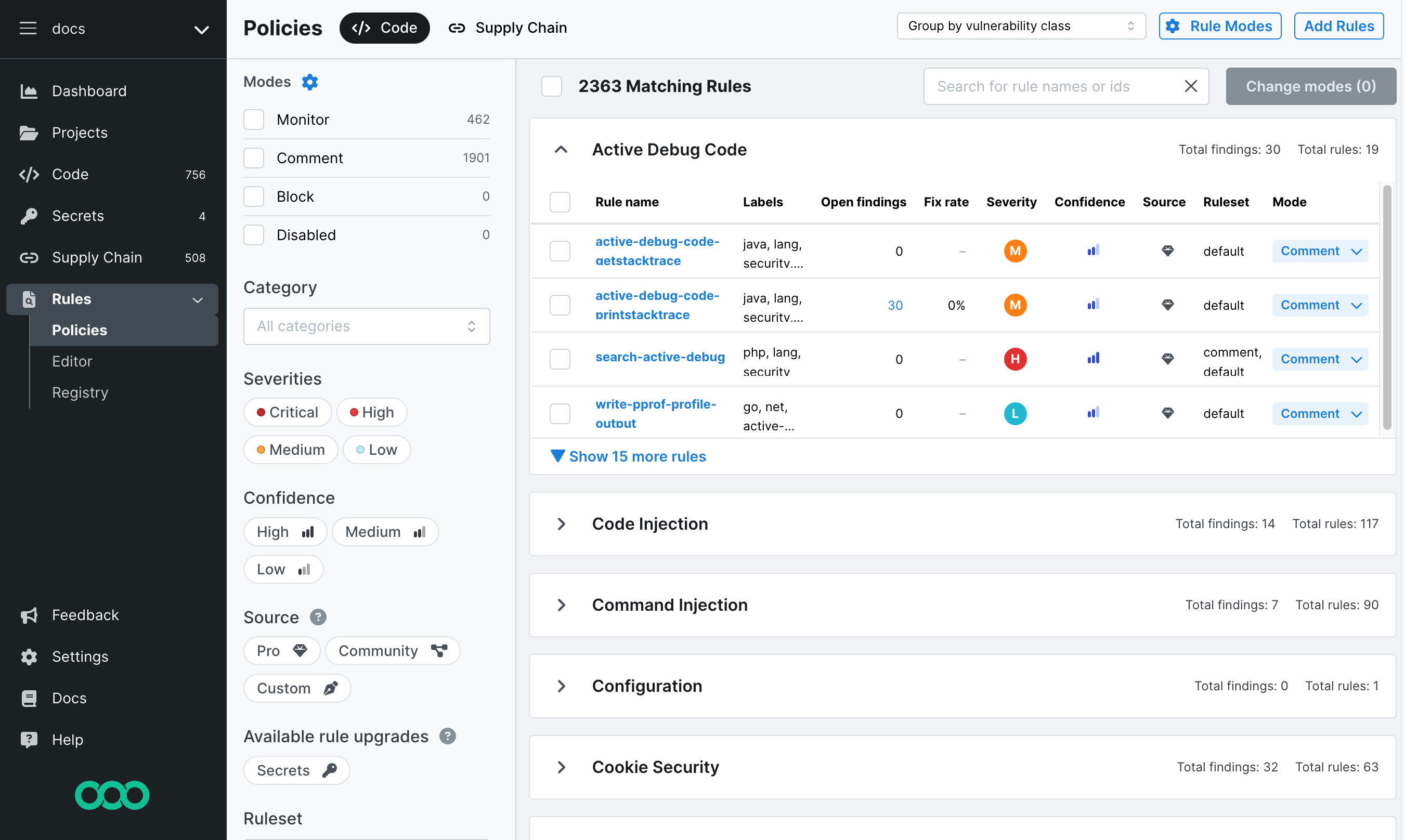
-
There is a new Policies page that is going to replace the Rule board in Semgrep Code! Switch to the new version by clicking Try new version in the Rule board header. The new page gives the rule overview a noticeable facelift and many optimizations, you can now easily filter for various types of rule metadata, and specific types of rules and make bulk edits which would have been hardly achievable with the old Rule board. Read more in Policies documentation.
-
You can now rename Projects in the Semgrep Cloud Platform. Before this update, when you renamed a repository in your Source Code Manager (SCM), for example in GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket, all of your previous Semgrep findings and triage data were lost as Semgrep recognized the renamed repository only as a new repository. With this update, you can now manually rename the project in Semgrep Code. This is the first step before we will bring you an automated solution (as this update still requires manual action). But now you can rename a project in Semgrep Code to match the new repository name without losing your findings data! To rename a repository:
- On the Projects page of Semgrep Cloud Platform, click the gear icon Settings. of the repository where you want to change the repository name.

- Click the three dots …, and then click Rename project.
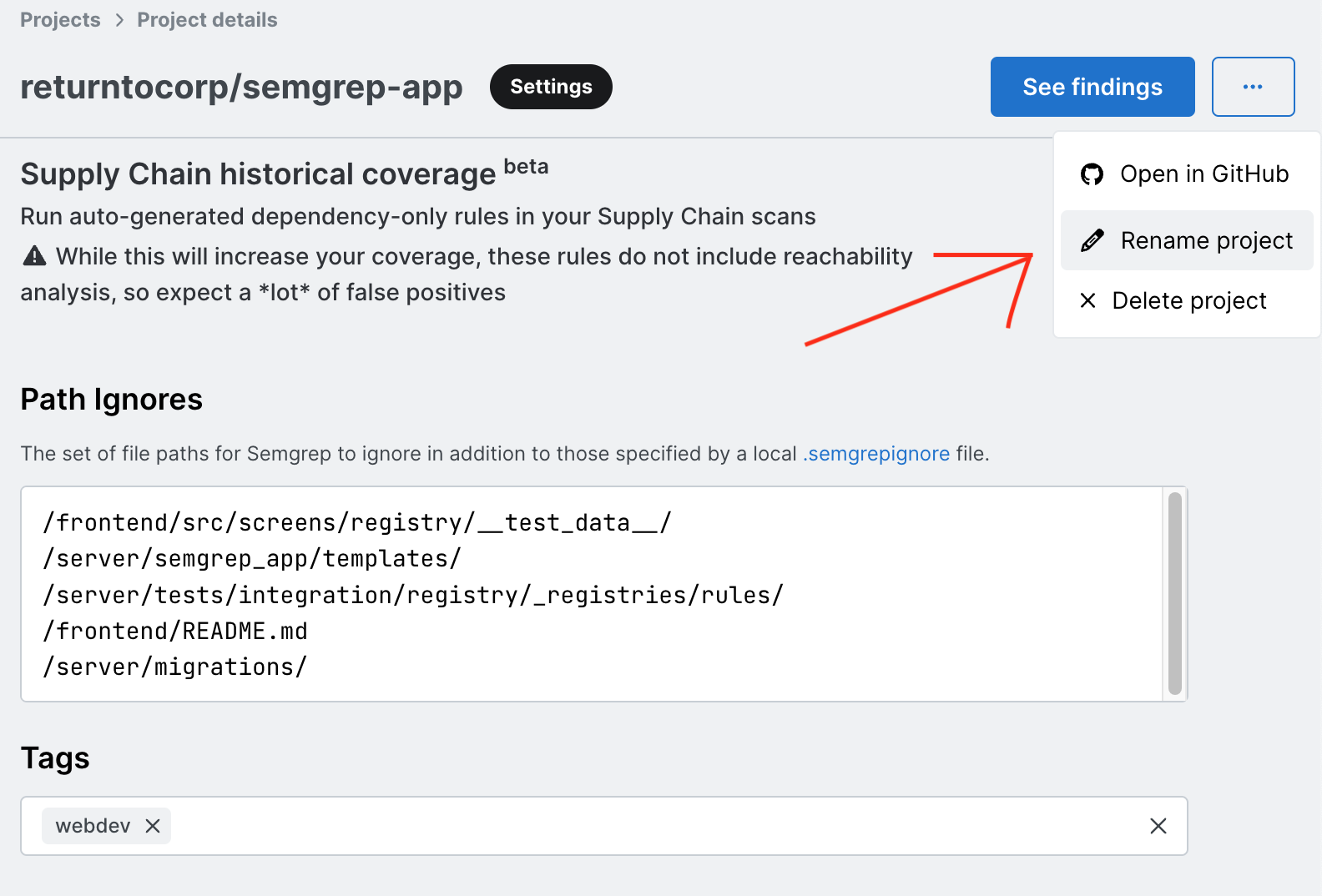
- Create a name that matches the name in your SCM, and then click Rename.
- On the Projects page of Semgrep Cloud Platform, click the gear icon Settings. of the repository where you want to change the repository name.
Pro rules
Recently released rules bring a total of:
- 61 Pro rules for Kotlin (with support frameworks like Spring and Ktor)
- 69 Pro rules for Go (with support frameworks such as Gin, Gorilla, gRPC, net/HTTP, and more)
These rules are available through the Semgrep Registry, in rulesets such as p/default and p/comment, as well as language-specific rulesets such as p/kotlin and p/golang. In total, there are now more than 500 Pro rules available.
Semgrep Pro Engine
- Semgrep Pro Engine now provides cross-function support for Go and Kotlin!
- Semgrep Pro Engine allows you to visualize the flow of tainted data (dataflow traces) in Semgrep Code. With this update, you can also receive findings with the visualized flow of tainted data in a pull request (PR) or merge request (MR) Semgrep comments. For more information, see the following documentation:
- Taint analysis:
-
Taint labels now mostly work cross-function (interprocedural) analysis, except for labeled propagators. Note that taint labels are experimental!
-
Taint analysis now supports cross-function (interprocedural) field sensitivity for JavaScript and TypeScript.
For example:
class Obj {
constructor(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
} -
Semgrep Pro Engine taint analysis can now perform field-sensitive analysis of class constructors in Java. For example, if the default constructor of a class
Csets its fieldxto a tainted value, giveno = new C(), Semgrep knows thato.getX()is tainted.
-
Documentation updates
Additions
- Added a new Usage limits FAQ page.
- Added a new document about License compliance.
- Added a new document Searching through your dependencies in Semgrep Supply Chain documentation.
- Added a new section Updating Semgrep Pro Engine in CLI.
- There is a new section Limitations of symbolic propagation.
- Added dataflow traces in PRs and MRs documentation.
- Add executing commands as strings and many more updates to the Command injection prevention for Ruby.
- Added Semgrep Pro Engine CI scans section.
- Added new Policies page documentation, also updated Rule board documentation with an admonition about Policies page.
- Added Semgrep Visual Studio Code extension documentation.
- Added Aliengrep reference documentation.
Changes
- Updated Join mode documentation.
- Admonitions regarding the new Turbo mode were added to Playground and Editor documentation. Go to Playground documentation and search for turbo mode.
- Updated Single-sign on (SSO) configuration.
- Updated Evaluating your security posture through the Dashboard document.
- Our Rule syntax document now shows that focus metavariables can be a list of more focus metavariables. See the rule example in Including multiple focus metavariables using set intersection semantics section.
- The General rule requirements section of Contributing rules document now includes a more precise definition of the
severityYAML rules key. - Our docs search now includes heading information to better contextualize search results and other fixes to optimize the documentation search.
- Code samples in Sample continuous integration (CI) configurations document now includes workflow dispatch and other additional updates to various code snippets on this page.
- Updated source paths in Contributing code documentation.
- Rule syntax table Language extensions and tags has been renamed to Language extensions and languages key values. The table has also been updated and is now accompanied by an introductory information and admonition.
- Removed
pattern-where-pythondocumentation as it was deprecated in Semgrep OSS Engine version 0.61.0. - There were also numerous typos fixed, many other docs pages improved, and some screenshots updated. All this is to improve your experience with our docs. Also big thanks to Parsia Hakimian for helping us to fix some of these typos!